
How can I use my company’s waste to create electricity and heat?
Get more out of your industrial waste.
The bottom line is important to all business owners. Being green is quickly gaining popularity. But, realistically you have to make green in order to even consider going green. One way to cut costs and increase profit is to flip the script on something all businesses create… WASTE!
Turning your waste into energy...
Gasification is just what the doctor ordered. It converts any well-sorted organic waste into heat and electricity. How you may ask? The waste is fed into the gasifier unit which breaks it down into a gas called Producer Gas. This producer gas can then be fed into a burner, which can create hot water through an existing boiler system. Or it can power an internal combustion engine, creating electricity!
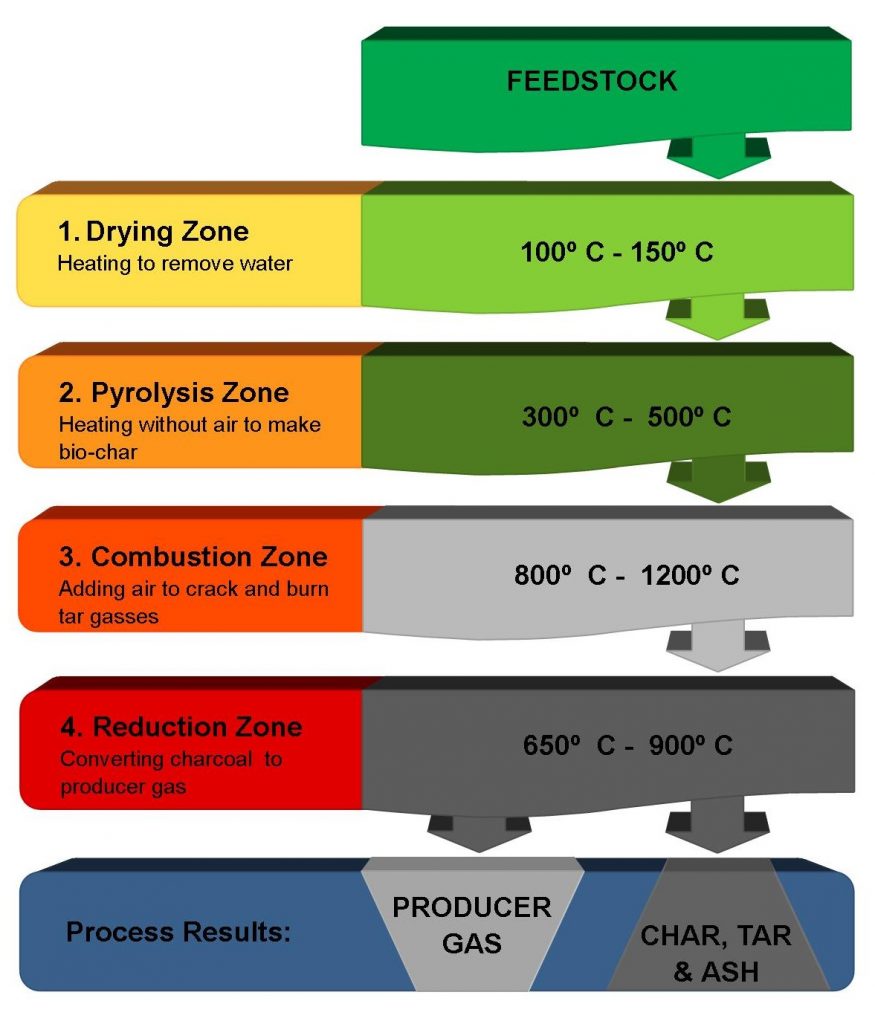
What types of waste can be used?
Gasification can be powered by any organic waste, meaning pretty much anything except for glass, metal, ceramics, dirt, sand, etc. Ideally, a gasification system is placed at the source of the waste production to keep the feedstock (waste) unmixed with inorganic components like the ones listed above. Here are some examples of the types of feedstock (waste streams) that can be used:
Medical Waste
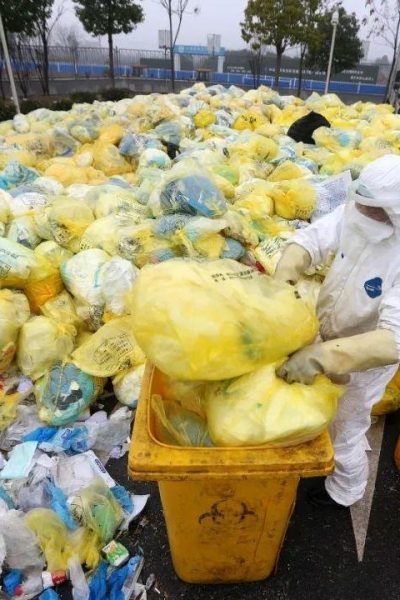

Medical waste is solid waste that is generated in the diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of human beings or animals, in research pertaining thereto, or in the production or testing of biologicals. A useable waste stream for gasification, excluding sharps, glass and metals. Examples include:
- Hazardous waste such as blood, bandages, swabs, gloves.
- Non-hazardous waste such as food waste, paper, cardboard, textiles, office waste, plastics.
Industrial Waste
Industrial waste is a general term used to describe material considered to be no longer of use after a manufacturing process has been completed. There are many sectors of industrial manufacturing that produce waste and sorted industrial waste makes an excellent feedstock for gasification. These include but are not limited to:
- Factories
-
- Shipping materials, organic process byproducts
-
- Mining
-
- wood, cartons, packages, food waste, plastics, rubber
-
- Textile mills
-
- fabrics, thread, shipping materials, packaging
-
- Food manufacturing
-
- food waste, packaging, contaminated cardboard, shipping materials
-

Agricultural Waste
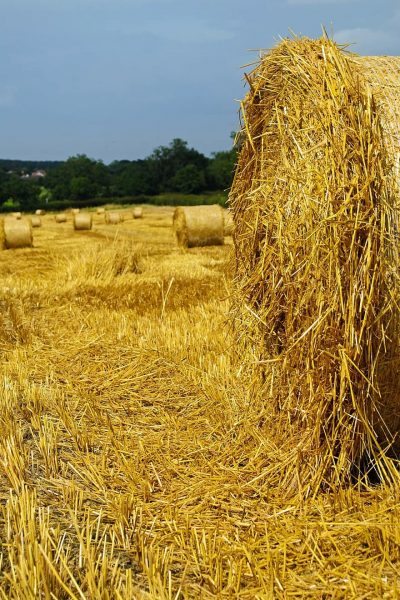

Agricultural Waste is unwanted or unsalable materials produced wholly from agricultural operations directly related to the growing of crops or raising of animals for the primary purpose of making a profit or for a livelihood. Examples include:
- Wood such as:
-
- logs, chips, bark
-
- Straw
- Agricultural (dry and wet) such as:
-
- poultry litter, animal slurry, and silage effluent.
- agricultural crop waste from crops like rice husks, cotton stalks, coconut shells, sugar beet, sugar cane, wheat and maize.
-
- Energy crop waste (dry and wet) such as:
-
- hemp, willow, poplar, miscanthus, switchgrass
-
Turn your waste into profit.
Gain from the benefits that downdraft gasification has to offer. By converting your waste into energy, you benefit three-fold.
- Cost Savings – By no longer having to haul your waste off site to your local landfill or costly hazardous waste management services, you save your business money.
- Energy Independence – Use your waste to create your own heat and electricity, reducing your utility costs and your dependency.
- Green Branding – A move toward sustainable on-site waste management gains you customers. Consumers are demanding more and more that companies be environmental stewards, choosing to support companies with green initiatives. Increase your revenue by gaining customers through being green.



